Family Offices: Wealth Management for the Ultra Rich
Have you ever brushed shoulders with a billionaire at your bank? Me neither. Read on to discover how the ultra-wealthy manage their money with family offices.
What Is a Family Office?
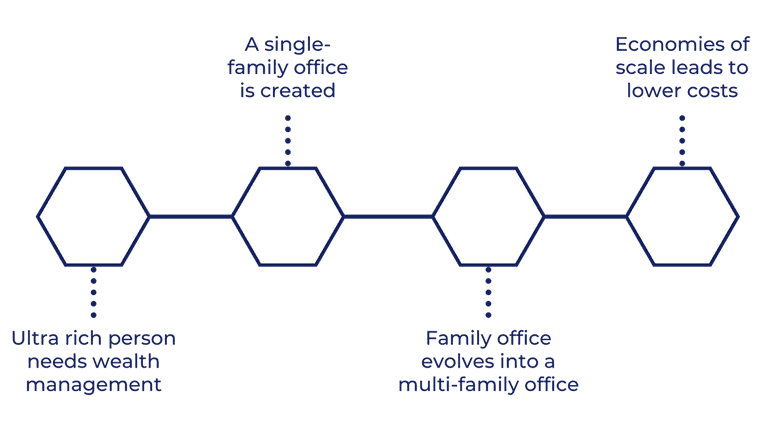
A family office is a full-service private wealth management firm that serves families with an “ultra-high net worth.”
Ultra-high-net-worth individuals (UHNWI) have at least $30 million in investable assets. At the end of 2019, there were 513,244 UHNWIs, and 47% of these wealthy families lived in the United States according to research done by Knight Frank.
There are two types of family offices: single-family offices and multi-family offices.
⭐ In 1882, the Rockefeller family founded a single-family office for their fortune. It still exists today and is now a multi-family office. You can read more about their legacy here.
What Do They Do?

Family offices are responsible for meeting all of the extensive needs of their client’s financial objectives while taking into consideration their risk tolerance.
Their overall goal is to maximize a successful family’s net return while strategically working with the family’s capital. Therefore, employees of a family office must specialize in a variety of services.
Here are some examples of the services that family offices provide:
Investment management
Perhaps the most classic component of a family office would be managing that family’s various securities and assets.
Creating an investment strategy: After evaluating the family’s overall financial situation, investment managers working for the family office are trusted to create the most profitable and viable investment strategy for the client. To accomplish this, investment advisors structure a well-diversified investment portfolio based on the risk tolerance unique to each investor.
Providing financial advice: Family offices provide financial advice for their clients' business ventures, and weigh factors such as expected return and volatility to ensure their decisions are well informed. For instance, investing in private equity can involve high returns but also high levels of volatility, whereas investing in real estate has low volatility but lower potential returns. All of these different investment options are available for families based on their individual risk tolerance levels.
Assessing and managing risk: Risk management is an extremely complex task that advisors are held responsible for. Determining a family’s risk tolerance has become an increasingly important job for a family’s financial advisors because recessions such as the Great Recession as well as the COVID-19 crisis have tested families' overall financial strategies.
Tax planning
Employees at a family office, including accountants and lawyers, ensure that their clients receive the most favorable tax treatment possible.
Tax code nuances: It is crucial for family offices to employ accountants and tax professionals to deal with a successful family’s taxes because there are many nuances to tax codes.
Tax rates across countries: Tax professionals are also well aware of the tax rates across different countries which is crucial for families who have their wealth chartered in more than one country.
Tax compliance: The tax planning team is also responsible for ensuring that everything that the family is involved in is tax compliant.
Philanthropic oversight
Combining a wealthy family’s personal goals with their professional goals often requires creating a charitable giving strategy.
Employees of a family office are responsible for designing a strategy that complements their clients' overall investment goals. Family offices can be responsible for the establishment of a family foundation, and overall advice regarding giving to charity and nonprofits.
Estate planning
Family offices within the estate planning service work to ensure that a family’s wealth will be maintained for the upcoming generations. Estate managers and lawyers are responsible for core estate planning which oversees handling family’s trusts as well as official documents such as wills.
In addition to the core estate planning, a family office provides advisory services to all of the generations in the family. This includes giving advice for the family’s professional and personal life. For instance, estate managers can provide financial mentorship to the younger generations which contributes towards the overall goal of maintaining a family’s wealth.
Estate planning is similar to succession planning, which focuses on the business that a family runs rather than all of the assets that a family owns.
Concierge
A concierge service is responsible for helping family members manage their busy lifestyles.
Services that fall under concierge include, but are not limited to, club (golf, private, etc.) memberships management, management of additional properties, private transportation, budgeting services, providing personal security, and so on.
Budgeting services are closely related to the job of the family’s wealth management team as the management of liquidity is integral to a family’s investment strategy.
In-House vs. Outsourcing
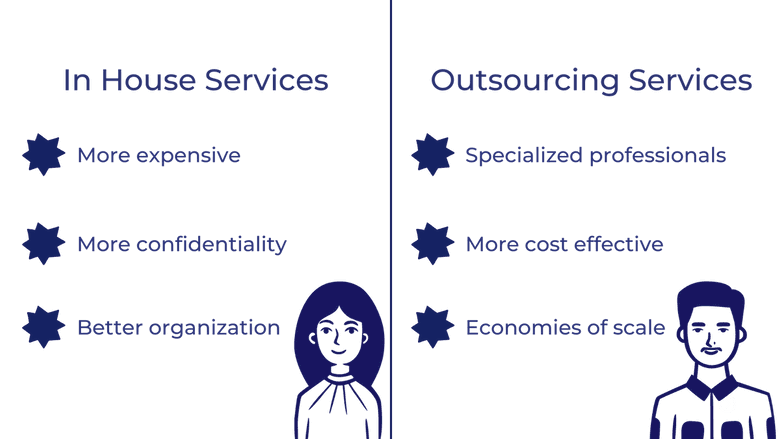
The above services are considered the core services of a family office. Outsourcing is an option that family offices can pursue if they do not desire to have all of their service providers in-house. In-house services vs. outsourced services both have their advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits of outsourcing services
Having some services outsourced can be more cost-effective and can demonstrate economies of scale.
Outsourcing can also allow the hiring of professionals who specialize in nuanced fields, whereas with having the service in-house, it may be more efficient to hire one professional who has a general grasp on many services.
Benefits of in-house services
On the other hand, having services in-house ensures the highest level of confidentiality which many families are willing to pay a premium for.
In addition, having services in-house can often consolidate a family’s finances and limit confusion.
Overall...
Oftentimes, the core services of a family office will be in-house, and any of the more specific needs of the family can be achieved by outsourcing.
Overall, the balance of which services are outsourced and which are provided in-house is up to the family’s needs.
Who Are They For?

As mentioned before, family offices are for ultra-high net worth families. There is no explicit lower limit to the amount of wealth needed in order to open a family office, but at least $100 million USD of manageable wealth is typical.
Families that have substantial wealth and are looking to preserve it for their next generations may consider opening a family office.
In addition, wealthy families that would benefit from family governance and overall organization would see use in a family office due to the “one-stop-shop” style of the business model.
Takeaways
- Overall, the opening of a family office is a tremendous deal due to the amount of wealth required to open one.
- Family offices are also becoming increasingly important as the wealth of many families has skyrocketed in the light of increased globalization and interconnectedness.
- For many families, the opening of a family office can reduce family conflict, and also increase efficiency by consolidating all of their financial services into one organization.
- Family offices are popular in sophisticated markets, but are not fully established in emerging markets. This can be seen as a weakness because it limits the accessibility of advanced wealth planning to only more developed economies.
The information provided herein is for general informational purposes only and is not intended to provide tax, legal, or investment advice and should not be construed as an offer to sell, a solicitation of an offer to buy, or a recommendation of any security by Candor, its employees and affiliates, or any third-party. Any expressions of opinion or assumptions are for illustrative purposes only and are subject to change without notice. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results and the opinions presented herein should not be viewed as an indicator of future performance. Investing in securities involves risk. Loss of principal is possible.
Third-party data has been obtained from sources we believe to be reliable; however, its accuracy, completeness, or reliability cannot be guaranteed. Candor does not receive compensation to promote or discuss any particular Company; however, Candor, its employees and affiliates, and/or its clients may hold positions in securities of the Companies discussed.
