What to Know Before Getting Your Hands on Bitcoin — A Complete Guide
Interested in purchasing Bitcoin? Or maybe you just want to learn more? Everything you need to know from the pros and cons to how to buy it.
While the mass population still holds many questions about the concept of virtual electronic currency, Bitcoin continuously attracts investors who see it as a new gold mine to dig.
Are you thinking about Bitcoin as your next investment purchase? Here is what you need to understand about Bitcoin and what to consider before getting your feet wet.
This article will breakdown:
- What is Bitcoin?
- How does Bitcoin work?
- Where Bitcoin's value comes from
- What is Bitcoin good for?
- Pros and cons of Bitcoin
- How to buy Bitcoin
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital currency that was launched in 2009 by an anonymous identity, under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Nakamoto published a whitepaper about the cryptocurrency on the P2P Foundation website, called "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System."
As the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin inspired the boom of hundreds of other new cryptocurrencies. Outliving the limited timespan of most competitors, Bitcoin still grows as a popular investment option.
Bitcoin has new underlying technology, operating principles, and upper-level applications. There has never been anything remotely similar in history. The main characteristics of Bitcoin are decentralization, globalization, and anonymity, discussed in more detail later.
The freedom of information associated with Bitcoins breaksBreaking the slow nature of information sharing, limitation of geographic locations, and international trading restrictions.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
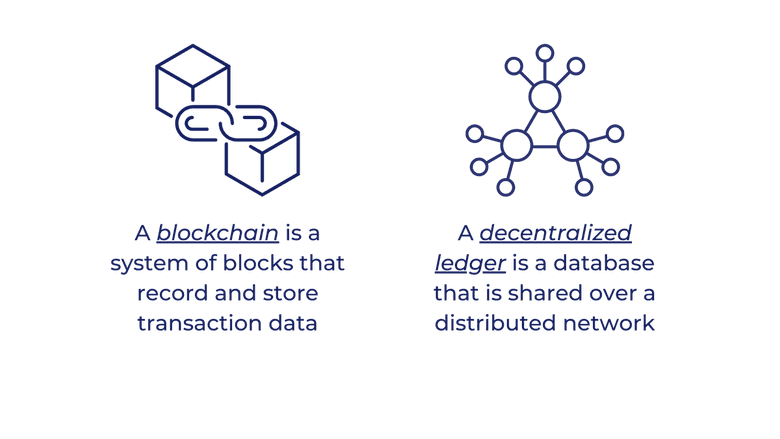
Blockchain
Bitcoin is managed by a large number of computers that run codes, data, and user information. The Bitcoin blockchain is a publicly shared, decentralized ledger, on which the entire Bitcoin network depends. A blockchain, put simply, is a system of blocks that record transaction data. All computers in the system are equipped with the same blockchain that contains the same blocks and transaction data.
Transparent
When one client makes a transaction in the Bitcoin software, the information system sends this transaction to the blockchain to be stored. Then, the transaction and new account information are synchronized with all computers in the system. This way, all computers share the same news that one transaction has been made, in turn, to provide transparency in each account.
Secure
Blockchain is not only transparent but also hard to breach on a security level. Blockchain is different from a typical database. Rather than just acting as a room to store data, blockchain also organizes data in chronological order.
Think of blockchain as a timesheet. There is a certain number of lines on a timesheet to fill out transactions. When one sheet (the block, in this case) is full, the next page (namely the next block) chains up with the previous information filled. There is no gap nor any chance to change the order of information. Each piece of information takes a fixed position at the exact time the transaction occurs. Put simply, blockchain is tamper-proof.
Decentralized Ledger
To even better demonstrate the working process, let’s compare and contrast the decentralized ledger (a.k.a. public ledger) system in Bitcoin with the old-fashioned centralized ledger.
Centralized ledger
A well-known form of the centralized ledger is a bank ledger. Each bank stores every transaction’s history and account information in a central database. This database is private from other banks and all its users, allowing each account holder to only view their personal account balance.
For example, a bank's central database states that Sam has a $0 balance and Bob’s store has a $3 balance. If Sam wants to scam Bob on a $5 order with a check:
- Sam writes the check, and Bob redeems it
- The bank verifies the check itself is real
- The request is processed, and the database shows: Sam’s balance: $0-$5=-$5, Bob’s store’s balance: $3+$5=$8
- The bank then determines Sam does not have enough funds to make the transaction, so the check is returned
- The system then states again: Sam’s balance: $0, Bob’s store’s balance: $8-$5=$3
Sam and Bob have no idea what the other person’s balance is. The action is only viewable through the central database which does not share access with the public. In this case, Bob cannot pre-determine whether or not to accept the check due to the lack of information.
Decentralized ledger
A decentralized ledger, however, promises transparency to users to eliminate scams or false transactions.
For example, in a household, all family members rely on their notebooks to record transactions between each other. The beginning of the page states that Mom has $5, and Dad has $3. If Mom gives Dad $3:
- Mom says she is giving Dad $3
- Everyone else verifies that it was Mom’s voice
- Each family member then writes in their notes: Mom’s balance: $5-$3=$2, Dad’s balance: $3+$3=$6
When you want to sell $5 lemonade to your parents, you will no longer go to Mom, but to Dad instead. This shared information allows you to make an educated decision on who to trade with.
The Bitcoin system is the family example on a macro scale. With blockchain as the foundation, anyone, including you and me, can monitor Bitcoin transactions live.
Where Bitcoin’s Value Comes From
The total number of Bitcoins issued is a fixed 21 million. Thus, the price of each Bitcoin is determined by the supply and demand principle in real-time. The higher the demand is, the higher the price is. The higher the supply is, the lower the price is. A competitors’ performance can also impact the price of a Bitcoin. Bitcoin’s pricing works the same way as any type of typical consumer product: when people want it, its value is expected to rise. A competitors’ performance can also impact the price of a Bitcoin.
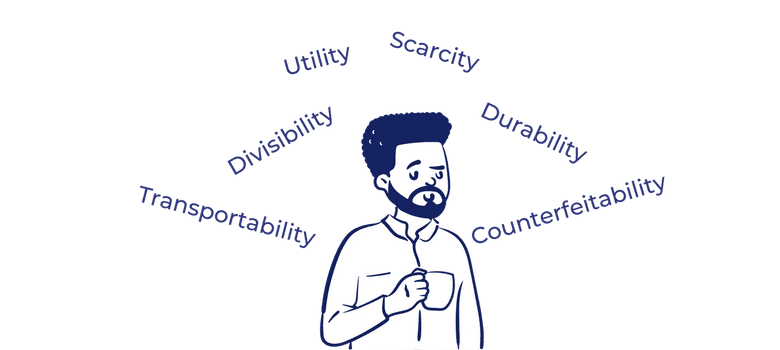
For any currency to hold value, it must satisfy 6 conditions:
- Scarcity
- Divisibility
- Utility
- Transportability
- Durability
- Counterfeitability
These main components provide sustainability for a currency and protect users from market disruptions from the creation of unauthorized currencies as well as duplication of existing currencies.
Bitcoin has value and is considered a currency because it checks all the boxes.
What Is Bitcoin Good For?
As many of the older generations have only recently accepted credit cards as their choice of payment, cryptocurrency pushes everybody out of their comfort zone.
What can a virtual coin be used for? This has been the predominant question for all interested parties.
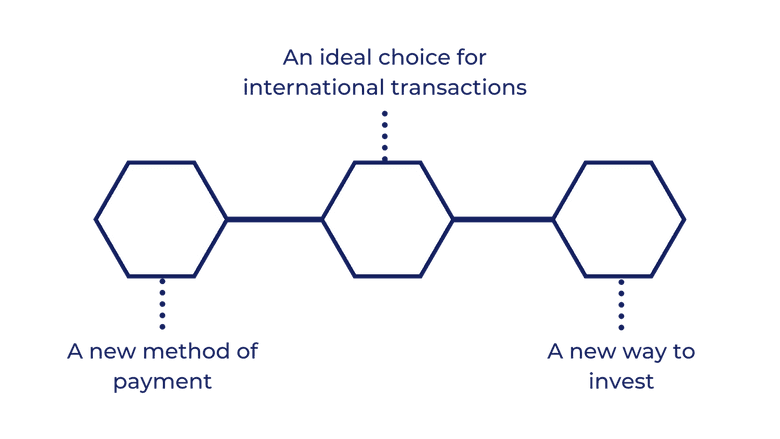
A New Method of Payment
One of the biggest uses for Bitcoin is its position as a fast, secure, and low-cost payment method.
Like Paypal and other online payment platforms, you can use Bitcoin as another debit card to pay online or in-store, to sellers that accept it.
Dell opened up Bitcoin payment back in 2014 and even promoted a 10% discount on all Alienware-brand products purchased through Bitcoin. Microsoft, Whole Foods, Etsy, Starbucks, Home Depot, Twitch, and many more companies announced their welcoming of Bitcoin in quick succession.
Although it is only a prediction that Bitcoin can be popularized in a timely manner, the trend shows Bitcoin is slowly becoming a substitute for easily broken or lost physical bank cards.
An Ideal Choice For International Transactions
Its benefit is especially outstanding when it comes to international transactions. If you have ever made an international payment through a bank transaction, you understand the high processing fees. The fees result from the cost to transfer funds across agencies. The consumer who makes the payment must cover all expenses reflected in inter-bank handling fees, domestic and/or international remittance fees, as well as conversion fees. Fees for cross-border payments by credit card can be as high as 3-4%, while the cost of using Bitcoin is only 0.5%~1%.
Additionally, countries like China have foreign exchange restrictions on how much you can transfer across the border yearly. Bitcoin is not affected by foreign exchange controls.
A New Way to Invest
Investing in valuable metals, gems, or antiques has been a common practice for some time now. The benefits of these investments are:
- They don’t disappear
- They hold value because they do not expire
- They allow you to hold as long or as short as you desire
- No regulation restrictions on the amount or frequency of trading
- The transactions yield little to no fees.
The popular choices of investment products such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and ETFs usually have expiration dates or regulations to follow when it comes to trading or liquidation.
Unlike stocks, investors in Bitcoin are not purchasing ownership of companies; it is a cash conversion from one currency to another. Such investment leads investors away from unsystematic risk within any particular industry or company. “Invest in what you know.” In this case, Bitcoin allows newer investors to avoid digging into specific fields in order to invest. Bitcoin is its own market. Free from governmental, social, and political influence, Bitcoin is also indifferent to systematic risks.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin
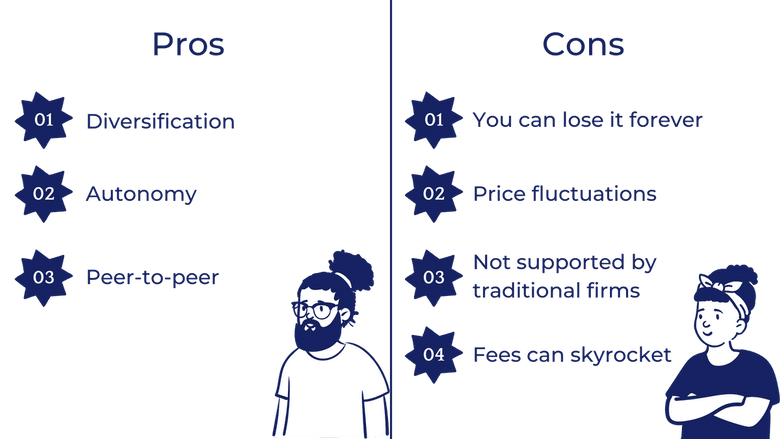
Pros
Cons
How To Buy Bitcoin

If Bitcoin sounds like something you want to get hands-on, here is what you need and how to get started.
To begin, you would need to set up a cryptocurrency exchange account, personal identification, secured network, and payment method. It is also encouraged to have personal banking accounts along with your exchange accounts. Make sure you have your government-issued ID due to the increasing restriction since 2020.
Step 1: Choose an Exchange Platform
Coinbase, Binance.US, Gemini, Coinmama, and Kraken are examples of popular platforms investors can choose from. Keep in mind, these platforms charge different fees and each has its own features. Investors can choose from any exchange that best fits their investment style. These popular exchanges do require KYC (Know Your Client) when used.
Step 2: Decide on a Payment Method
Once you have successfully registered for an account, you will be required to submit identification information to verify your legal identity and proof of income in some cases. The forms of documentation you may need are subject to change based on the laws in your country and/or region. It can be expected that you will need a government-issued ID or SSN, proof of income, and employment information. You may also need to disclose your residency information. Purchasers can refer to their brokerage account setup process.
Bank accounts, debit cards, and credit cards are all acceptable methods of payment. Credit cards are not highly recommended for this type of purchase due to the unpredictable outlook and potential interest rate. A transaction fee comes along with credit card purchases as well and will depend on your bank’s policy.
Step 3: Make Your Purchase
Nowadays, exchange platforms have simplified their services to be easy to navigate. Once your account and payment information are all set, you can start your purchase.
Bitcoin can be purchased as a whole or as a fraction of shares. In some exchanges, you are offered market and limit orders. Some exchanges also offer stop-loss limits for their users. To top it off, platforms such as Coinbase provide the option to dollar cost average and reinvest in desired products on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis.
Step 4: Choose a Hot or Cold Wallet
A cryptocurrency wallet is doubly secure to ensure the safety of your assets. It keeps your private key in the system while creating a trustworthy place to store your cash outside of the exchanges in case of a security breach. There are a variety of wallets users can choose from, the two typical types are hot wallets and cold wallets.
Hot wallets are online products you can access through the internet on your computer or mobile devices. The selling point is accessibility. The drawback is that if the internet used to log into the account is not secured, hackers can steal users’ private keys and access accounts. For those who prefer online access, storing a small amount of your total wealth for only what you need may be the best choice.
Cold wallets are offline wallets or hardware wallets. The access does not require the internet which closes the window for online crime opportunities. They usually take the form of portable devices like USBs that download users’ private keys and Bitcoins. Another old-fashioned but perhaps the most secure way to store is a paper wallet. You can generate paper wallets on certain websites that produce both public and private keys. This piece of printed paper can be locked away with other valuables. It is also not a bad idea to back it up on your devices.
Bitcoin Mining
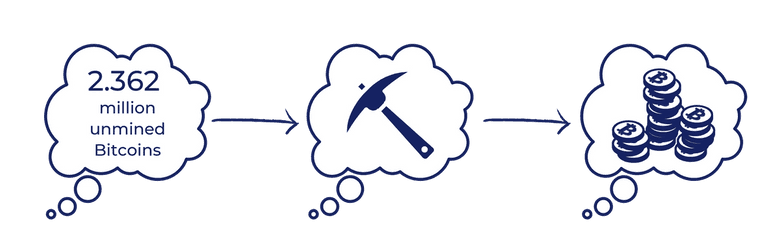
Aside from purchasing Bitcoins with cash, some people turn to Bitcoin mining. There are 21 million Bitcoin total available, but they are not all issued at once. So far, 2.362 million Bitcoins are still yet to be mined: thus, not circulating on the market.
Mining unlocks the remaining Bitcoin, while also protecting the security of the Bitcoin system. The creation of Bitcoin began with solving a series of extremely complex algorithms. At the root of it, it’s all mathematics and matrixes. The miners use specific highly functional computers to complete calculations that result in the formation of a block in the blockchain. When miners decode a unique equation, the system pays the miners in the form of a Bitcoin. This is how the entire complicated system operates.
The main function of the platforms is peer-to-peer payment. Without a centralized agency, namely banks, to record all transactions, miners take the role of the accountant to record data with coding.
Bitcoin mining became a new way to build wealth by technology professionals. However, the designated equipment and time invested in it can cost you a fortune. The time used to mine a Bitcoin is approximately 600 seconds, but the solution to the equation you get is likely not correct. Let alone the upfront investment can cost you a fortune, many professional miners spend months without any accomplishment.
Takeaways
It is understandable that many investors hold suspicions about cryptocurrencies. While the price of Bitcoin seems to be a roller coaster, “digital gold” opens a door to possibilities in the future. Although the newness needs more time to permanently secure its position as a counterpart of fiat currency, its popularity and benefits as both a payment method and investment should not be overlooked. With smart investment decisions and careful research, investors can consider Bitcoin as the next product in their portfolio.
A decade into launch, cryptocurrencies still have a long way ahead to fulfill the prophecy of standing on equal footing with fiat currencies.
The information provided herein is for general informational purposes only and is not intended to provide tax, legal, or investment advice and should not be construed as an offer to sell, a solicitation of an offer to buy, or a recommendation of any security by Candor, its employees and affiliates, or any third-party. Any expressions of opinion or assumptions are for illustrative purposes only and are subject to change without notice. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results and the opinions presented herein should not be viewed as an indicator of future performance. Investing in securities involves risk. Loss of principal is possible.
Third-party data has been obtained from sources we believe to be reliable; however, its accuracy, completeness, or reliability cannot be guaranteed. Candor does not receive compensation to promote or discuss any particular Company; however, Candor, its employees and affiliates, and/or its clients may hold positions in securities of the Companies discussed.
