Ethereum: Everything You Need to Know to Start Investing
If you're looking for a cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin, you might have considered Ethereum as a cheaper alternative. Here's everything you should know.
You're probably familiar with Bitcoin, but are you familiar with one of its biggest competitors, Ethereum? Or, if you are considering investing in Bitcoin or Ethereum, do you know the differences?
This guide will cover:
- What is Ethereum?
- How does it work?
- How does it compare to Bitcoin?
- Pros and cons
- How to invest
What Is Ethereum?

Vitalik Buterin came up with the idea of Ethereum in 2013. After a round of funding in 2014, the Ethereum network went live on July 30th, 2015.
Like Bitcoin, Ethereum is also a decentralized blockchain network. It holds its own cryptocurrency called Ether, ETH. ETH emerged as a dark horse after Bitcoin, and it’s now commonly said to be the second most popular cryptocurrency. Ether is given the nickname “Bitcoin 2.0”.
Ethereum is not to be confused with Ether. Ethereum cannot be owned by anybody. It is a decentralized network. This network was built upon the idea of taking thousands of computers around the world to form a giant supercomputer. Ether is the blood that runs through the entire body of Ethereum. It is a digital currency being traded as an investment, but also the form of the wage for the miners.
How Does It Work?
The magic of blockchain
If you are interested in cryptocurrency, you’ve probably heard of blockchain. Let's take a look at what it is and how it works.
A general explanation of blockchain
Blockchain is essentially a decentralized database — a series of data blocks associated with cryptographic methods. Each data block stores information about a transaction, which is used to verify the information and generate the next block.
In a narrow sense, a blockchain is a chained data structure that combines each block in a sequential manner and is a distributed ledger that cannot be tampered with. Once each block is connected to the blockchain, information stored inside cannot be changed forming a perfect transaction history. Broadly speaking, blockchain technology uses calculation methods for programming and manipulating data with smart contracts composed of codes.
A look at blockchain in regard to Ethereum
Ethereum is powered by blockchain technology providing a public ledger where all financial data and agreements can be verified and stored in complete transparency. The whole process is done via software without interception by any named organization.
The Ethereum blockchain technology is not the same as the Bitcoin network. Ethereum's network is composed of thousands of computers around the world, called nodes, creating security for the data. Even with one computer down, it does not put users’ information at risk because all other computers are holding up the network. Hackers must take down 51% of all nodes to overwrite information already stored in the blockchain — that is 51% of thousands of computers in the world.
Behind the scenes: miners
Smart contracts
Behind the operation of Ethereum, there is a community of people to maintain it, called miners. ETH miners generally work similarly to Bitcoin miners. They are bound by smart contracts (smart contracts are self-executing contracts). The agreement between parties is directly included in written codes — the code is the central control of the contract which exists within the entire blockchain network. Smart contracts take place anonymously between each party.
The bright side of the smart contract is that the contract takes place, executes, and finalizes without the supervision of any named authority, legal system, or external witnesses. Miners around the world are able to dive into work while maintaining the privacy of their identities. It is the true representation of a decentralized network.
Finding the unique code
There is a 64-digit unique code for each block, and miners must find the correct code to complete their work. Miners validate each block before it’s put up in the blockchain to store transactions, and they receive the reward of ETH for their work once finished.
"Gas" fee on transactions
To understand where ETH came from, we need to know that there is a fee called “gas” associated with each transaction. “Gas” is paid to the miners to ensure the current miners stay on the job while encouraging new miners to join the team. Other than being paid as a wage, “gas” limits the number of actions a user can complete in one transaction, as well as being a fence for network scams.
However, because one block can hold only so many gas fees based on the amount and type of transaction, the gas fees may be pretty high due to the network activities. Miners would rather choose transactions with higher gas fees to approve first, which leads to competition between users and traffic in the network.
Decentralized ledger
Throughout this article, you will repeatedly see the word “decentralization.” Let's look at what it is and why a decentralized ledger is essential in the working of cryptocurrency.
But first, let's look at what centralization means...
Now let's look at decentralization
In the decentralized world, there is no authority, which ensures peer-to-peer trading with cryptocurrency. Decentralization helps to work toward financial freedom from regulation. Just like selling something online, you are able to sell or buy without the need to meet the other party, nor go through an authorized party to confirm the transaction.
In a decentralized ledger, no one has absolute control over any information because it’s a network built by a community. This ensures users’ privacy but also has the ability to prevent scams. If you have ever heard of someone receiving a fake or bounced check, you can be sure that this does not happen here.
At the end of the day, the goal of cryptocurrency is to provide financial freedom. Whenever a centralized power steps in, we give up a certain control of our privacy and money. Decentralized finance allows a permissionless and interoperable environment for investors they wouldn’t have under centralized markets.
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin
Ether is not intended to replace fiat currency
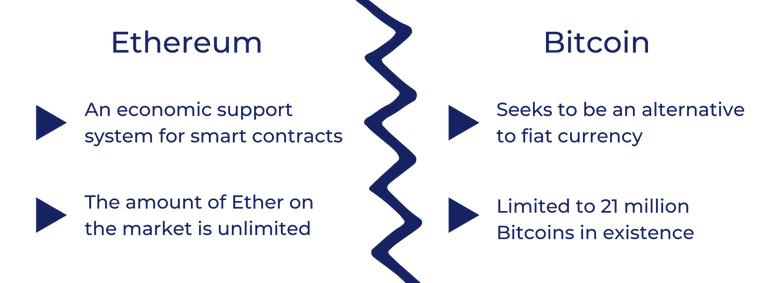
Bitcoin is more so a store of value, like gold, simply existing as a cryptocurrency. Although Bitcoin is widely considered an investment, its primary goal is to be used to purchase goods and services. At its root, Bitcoin seeks to become a replacement for fiat currency. It holds more similarities to fiat currencies, especially because of the limited 21 million Bitcoins in existence.
Ether, however, was never intended to replace fiat currency. In fact, Ether was never born under the expectation of being an alternative monetary system in the market. Rather, it is an economic support system behind Ethereum’s smart contract with the decentralized application (DApp) platform.
Ether acts as wages and is unlimited
Although Ether is currently being traded and used like Bitcoin, Ether also has the mission of acting as wages in Ethereum’s smart contract. Such a payment method does not require Ethereum to hold large funds for employees’ wage payables. Being a decentralized operation, Ethereum doesn’t operate with a physical office and management. By utilizing Ether as the reward for labor, Ethereum is free to make contracts with any talent across the world.
Therefore, the amount of Ether on the market is unlimited, unlike Bitcoin. Basically, Ether allows Ethereum to self-generate, self-operate, and self-support the entire decentralized application free from the limitation of a centralized business system.
The Good & The Bad
PROS
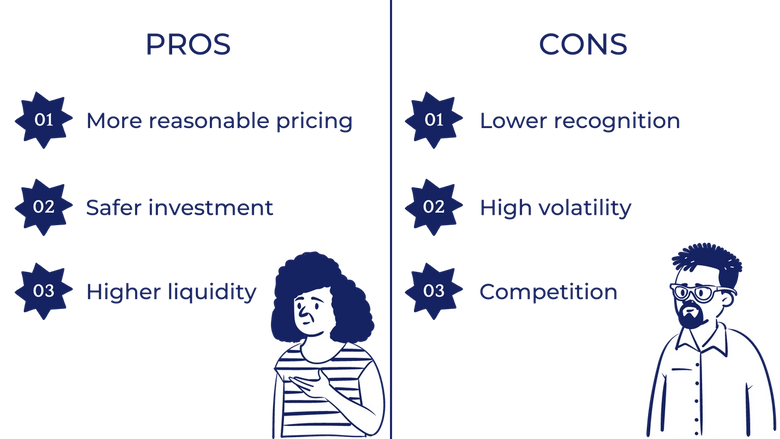
Relatively reasonable pricing
Ethereum’s pricing is much more affordable than Bitcoin. While one Bitcoin can go for over $50,000, Ethereum’s all-time high value for one coin was only $4,362.35. In this sense, investors do not have to lock up as much capital in the cryptocurrency market, and they can hold more Ethereum coins in their pockets.
Without a limited coin amount, investors generally do not hold Ether as long as they hold Bitcoins. As a result, it is less likely to hype and dump Ether in the supply market to influence the price as hugely as it affects Bitcoin.
Safer investment
As we previously discussed, Ethereum is a decentralized platform, unlike banks or government agencies that have centralized servers. If your bank account has ever had unauthorized charges, that is the disadvantage of centralized servers. Ethereum’s blockchain system allows information to be verified, then stored in a particular way. Once information is recorded, no one has the power to change that, meaning your information will be entirely safe.
To hack the Ethereum server, hackers need to control over 51% of the nodes to enable information editing. With thousands, if not hundreds of thousands of nodes holding up the network, hacking is nearly impossible.
Even safer than Bitcoin, Ethereum has a larger community of active developers around the globe who are operating the system. In the world of blockchain, the popularity of the developer means the security level of the system.
Higher liquidity
Ethereum has the upside of any cryptocurrency: liquidity. Compared with stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, cryptocurrencies are much more liquid.
Crypto trading is different than stock trading in that cryptocurrency doesn’t have an organized exchange market, and the price of the coins is always changing. Since the market doesn’t close at any time, investors can always monitor their investment and make trades, sales, or purchases whenever they please.
CONS
Lower recognition
While Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency out on the market right now, its popularity is incomparable to Bitcoin. Bitcoin has grown to be one of the biggest names in the world of investment.
In the future, investors may face the challenge of a shrinking market, making selling more difficult. Investors may have capital locked up if they have trouble getting rid of coins during a downturn.
The demand for Ether could decrease from the future growth of Bitcoin or the rise of other popular cryptocurrencies. Ethereum stands at a crossroads: it has the potential to glow or fall.
High volatility
One unavoidable aspect of cryptocurrency is volatility. Many argue that the high volatility of Ethereum and other crypto investments make them unsuitable in a portfolio. In the month of May 2021, the highest price of one Ether coin was $4,337.93. However, it went as low as $2,139.96 in the same month.
The risk of losing principal may be greater than the chance of making a big buck. However, the price falls can be a good time for new investors to migrate into the market.
The cryptocurrency market typically requires an aggressive risk tolerance and good timing. Those who jumped into this market early have the ability to take on price fluctuations. For the average investor, carefully judging when and how much to invest in Ethereum can be important. The most basic investment principle still stands: “buy low, sell high”.
A lot of competition
Competition creates a fair market, but it often brings bad news for investors. In the past decade, many other cryptocurrencies have emerged, such as Ether (ETH), Stellar (XLM), Binance Coin (BNB), Cardano (ADA), etc.
Bitcoin is Ethereum’s biggest competition, and regardless of its high price, Bitcoin has outlived much of its competition. Aside from Bitcoin, Cardano, commonly acknowledged as the third popular cryptocurrency, may also pose a threat to Ethereum. Cardano’s all-time high price was only $2.9682 recorded on September 2nd, 2021.
Ethereum is arguably in an awkward position today. On one hand, Ethereum is not nearly as well-known as Bitcoin, and Bitcoin is likely the first choice of investors with higher financial abilities. On the other hand, Ethereum faces early-stage competitors that are more affordable. Investors wishing to test the market are more willing to invest a small amount, meaning Ethereum may not be as economically competitive.
How To Buy It
Buying through a centralized exchange
1. Choose an exchange platform
If you prefer a centralized exchange to make your cryptocurrency purchase, you first need to choose an exchange platform. Examples of some big ones are Binance.US, eToro, Kraken, and Coinbase. There are many popular exchanges now offering cryptocurrency services.
2. Set up an account
After choosing your exchange, you need to set up an account. The information you need is very similar to what is required of any brokerage account. Your full name, government-issued ID, and social security numbers are the must-haves. Based on your region and local law, you may also be required to disclose your residence address. On most exchanges, credit cards, debit cards, and bank accounts are all acceptable methods of payment.
3. Choose a wallet
There are two types of wallets: hot wallet and cold wallet. The hot wallet is generally online, and you need the internet to access it, which can increase the risk of hacking. The cold wallet is the digital storage of your coins that does not require an internet connection to access; they are most commonly seen in the form of a USB device or a download of files on your hard drive.
4. Purchase Ethereum
Finally, you will be all set to purchase Ethereum. One thing to note, exchanges make a majority of their profit through fees. When making trades or cashing out coins, be sure to include the fee liability into account.
Buying through decentralized exchanges (DEXs)
For people who are drawn to the anonymity of crypto, DEXs give you more control over your assets because you don't need to go through a centralized agency or deposit your coins into your trading account. Your trade is anonymous and entirely private.
1. If you have a wallet, you can trade through DEXs
If you already have your own wallet, you can purchase or trade Ethereum directly through decentralized exchanges, allowing a true peer-to-peer (p2p) exchange.
2. Choose the right exchange
Think of DEXs as eBay for cryptos — you trade directly with other investors. Waves DEX, Bisq, Dexguru, and 1inch exchanges are some examples of DEXs out there.
As there are many decentralized exchanges for investors to choose from, this ranking for decentralized exchanges with trading volume data may be useful.
Warning: make sure you understand DEXs because they can be complex for beginners
Unfortunately, DEXs are more complex to navigate for beginners. The main use of DEXs is to trade one cryptocurrency to another, rather than buying Ethereum directly with cash. If you wish to trade your other cryptocurrencies for Ethereum, it is definitely a choice to consider.
Takeaways
Ethereum, although similar to Bitcoin in its nature, is operated very differently with improved technology. Ethereum is also more affordable for investors who do not want to pour nearly a year of wage into the crypto gamble pool. However, keep in mind that Ethereum holds all the risks of cryptocurrency as much as the advantages. Making smart and educated decisions will take you a long way.
The information provided herein is for general informational purposes only and is not intended to provide tax, legal, or investment advice and should not be construed as an offer to sell, a solicitation of an offer to buy, or a recommendation of any security by Candor, its employees and affiliates, or any third-party. Any expressions of opinion or assumptions are for illustrative purposes only and are subject to change without notice. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results and the opinions presented herein should not be viewed as an indicator of future performance. Investing in securities involves risk. Loss of principal is possible.
Third-party data has been obtained from sources we believe to be reliable; however, its accuracy, completeness, or reliability cannot be guaranteed. Candor does not receive compensation to promote or discuss any particular Company; however, Candor, its employees and affiliates, and/or its clients may hold positions in securities of the Companies discussed.
