Cardano: Get to Know this Dark Horse in Crypto
Considering getting involved with a cheaper, less established cryptocurrency platform? Here's everything you should know about Cardano.
With so many emerging cryptocurrency options out there, you may be struggling to decide what's right for you. While you're probably familiar with Bitcoin, you may not be with some of the less established crypto platforms. Have you heard of Cardano? Let's explore how this cryptocurrency platform stacks up against the rest.
This article will cover:
- What is Cardano?
- How it works (comparing PoW and PoS)
- Pros and cons
- How to get started
What Is Cardano?
Cardano is a decentralized blockchain platform founded by Charles Hoskinson (also the co-founder of Ethereum) and launched in 2017. Transactions on Cardano are facilitated by its inner cryptocurrency, ADA.
Hoskinson targeted Ethereum’s weaknesses and improved them in the design of Cardano. Compared with the big two in the crypto market (Bitcoin and Ethereum), Cardano has its own unique set of advantages:
- First, Cardano is more energy efficient, and capable of instant transactions with minimal fees. The minimization of fees alone allows Cardano to stand out compared to Ethereum, which can cost you a hefty gas fee when getting your trade approved by miners.
- Second, Cardano has a cap of 45 billion coins outstanding. In comparison with the 21 million Bitcoins outstanding, Cardano attracts more validators. Also, because the limited cap creates a certain but not intense scarcity, Cardano is more than just a store of value.
How Does it Work?
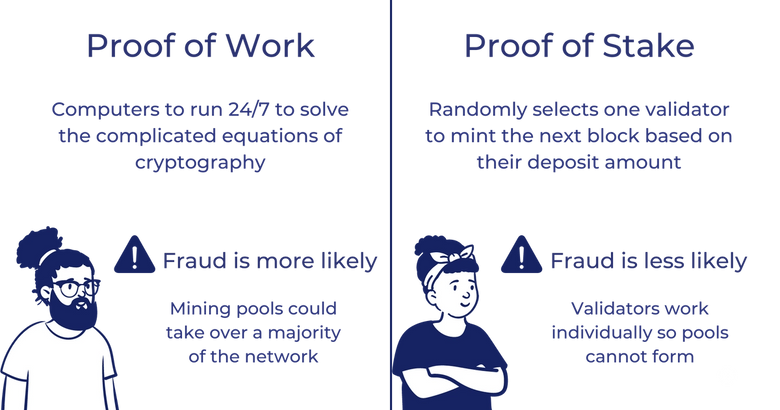
Bitcoin and Ethereum 1.0 both use the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to verify transactions and load them into the blockchain to generate new tokens. In comparison, Cardano and Ethereum 2.0 use Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Although the PoW method once worked like a charm, the PoS mechanism is much safer, fairer, and more energy efficient.
Proof of Work
The concept of Proof-of-Work (PoW) was first introduced in 1993 to combat spam emails. The technology had been mostly forgotten until the founder of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, picked it back up. PoW allowed Nakamoto to solve the problem of verifying transactions without a third party. PoW answered another question for him, “How do we make sure no one can make more than one transaction with the same fund?”
How PoW works...
Underlying PoW is advanced mathematics called “cryptography.” Cryptography uses complex mathematical equations that can only be solved by extremely powerful computers. Each set of equations is unique, meaning once the transaction is approved, it is set and done without the possibility to override or edit it. Therefore, once each transaction is verified, the information will be updated and stored. It eliminates the chance for people with bad faith to make multiple transactions with the same fund.
What are the disadvantages of PoW?
You can imagine how much energy power is required for computers to run 24/7 to solve the complicated equations of cryptography. Moreover, this mining system gives an advantage to miners who have more equipment. People with a single set of mining computers are less likely to be rewarded due to their lack of ability to compete with large mining firms or mining pools around the world. Why? Because only the first miner to solve the algorithm gets the reward.
The disadvantages of PoW don’t stop here. To create a malicious block in the PoW blockchain system, the miner needs to control 51% of the network. It sounds difficult to gain control of that many computers, right? Well, as the competition gets steeper due to the decreasing number of coins left to mine, many miners have given up on the PoW system. When fewer computers are powering the operation of the PoW network, big-time miners from mining firms or mining pools have a better chance to take over a larger percentage of the network. The existence of mining pools makes the network more centralized rather than decentralized.
Proof of Stake
To solve the issues of PoW, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) emerged as a new consensus mechanism. In the PoS system, miners are replaced by validators. Simply put, PoS randomly selects one validator to validate the next block. This eliminates energy waste because people do not have to compete to solve the same equation. To be considered a validator, each person, called a node, has to deposit a certain number of coins into the network. It’s very similar to the security deposit you put down when you rent a residence. The amount of the deposit decides the chance that each validator will be chosen to mint the next block.
What if a validator approves a fraudulent transaction for the reward? Remember the deposit of stake they put down upfront? With each falsely approved transaction, the validator loses a part of their stake in the network — the same as a portion of your security deposit being deducted when if punch a hole in the wall in your apartment. Validators would lose more money than they gain, making the gain from false approvals far less than worth it.
Fraudulent activities are less likely to happen in PoS. This system does not allow or encourage people to team up as a pool. In PoW, people can team up in order to take the majority of the nodes causing potential danger. There is simply no need to team up with anyone else in PoS because no two nodes are working on the same algorithm. The network is more decentralized this way and thus, more secure.
PoS is safer for the users because it requires more elements for attackers to attack the network. In PoW, you need to control 51% of all nodes, so if the largest few mining pools in the world were to combine their power, they may be able to control the entire network. However, to override the system in PoS, one individual must hold over 51% of all cryptocurrencies in the network. For coins like Cardano that have a huge number of coins outstanding, holding 51% of all coins requires money and power that hardly anyone has.
Moreover, even if the attackers were to purchase all these coins from the open market, they are creating significant scarcity. In turn, the more coins they purchase, the higher the price will be. At the end of the day, they could spend much more money on purchasing the coins to control the network than their gain on approving fraudulent transactions. When they decide to sell the coins again, all of the coins flying back into the market will cause a surplus that reduces the value of each coin. The loss on selling the coins back alone is enough to stop most from even thinking about an attack.
The Good and The Bad
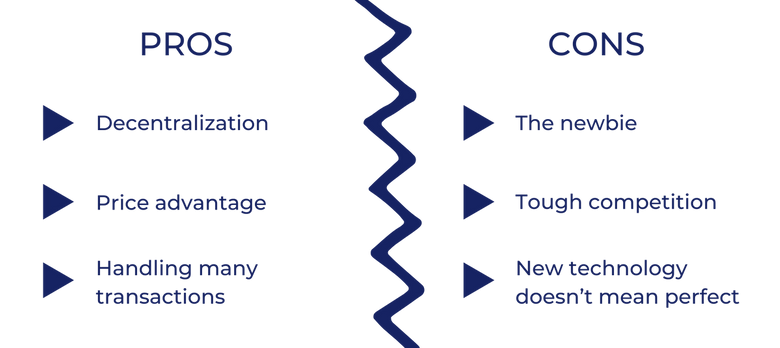
PROS
Decentralization
You may think that all cryptocurrencies are decentralized, but not all of them are as decentralized as they are supposed to be.
Whether a cryptocurrency is truly decentralized depends on whether it uses PoW or the PoS:
- PoW is more centralized: These crypto networks, such as Bitcoin, force miners to centralize their computer power to generate a profit from mining. PoW leaves individuals with nearly no chance to earn rewards on their own as fewer coins become available.
- PoS is more decentralized: Cardano’s PoS presents a much more decentralized platform for investors. With validators around the world working independently on their assigned blocks, it eliminates the possibility for people to centralize their power.
Price advantage
One advantage of Cardano is the affordable price point. It’s no secret that many investors find it difficult to pay the high prices for Ethereum or Bitcoin. Cardano’s price first broke the $1 mark in February 2021. As of October 2021, the highest price is $2.9682 per coin, which is affordable for most investors.
With that being said, Cardano's price has the potential to rise. In the first 2 months of 2021, Cardano’s price increased by 720%. So far, its price has remained relatively stable at above $2. The saying typically holds true that cryptocurrency is the investment you want to hop on when it’s still early. With many early Bitcoin and Ethereum holders making good returns, investors may consider investing in Cardano before it potentially experiences rapid growth.
Handling many transactions
If you read about Ethereum 1.0’s disastrous transaction traffic, you might appreciate Cardano’s ability to handle large numbers of transactions. As active user bases grow, popular cryptocurrencies often face the problem that more transactions are made instantaneously than they can handle.
Bitcoin can process 10 transactions per second and Ethereum is capable of processing 15 per second. Whereas Cardano can approve 257 transactions per second, the advantage is obvious.
An increasing number of investors are interested in crypto arbitrage because of its freedom from regulations. Some of you may consider selling relatively fast after acquiring coins as well. In the crypto market, a few minutes of delay can cause prices to change in an unfavorable way. The fluctuation may not be big, but for arbitrage investors and people selling in big values, it can be quite a concern.
CONS
The newbie
While Cardano has shown growth in the past 6 years, there's also a good chance Cardano is not the first name popping into your head when you think of cryptocurrency.
Stocks and cryptocurrencies alike, penny stocks, or newer cryptocurrencies may be affordable to purchase, but any price fluctuation involves a higher percentage of gain or loss on your principle. Because of this characteristic, investors may find themselves in need of getting rid of coins quickly. With lower recognition, Cardano may not have as high of a demand on average. You could end up with coins sitting in your wallets longer than you intend.
Tough competition
The cryptocurrency market is always a tough battlefield. Especially in the past 3 years or so, more and more crypto products have been launched. For Cardano investors, the intense competition may be a bitter pill to swallow. Aside from going head-to-head with Ethereum and having Bitcoin as a giant rain cloud, Cardano is also in the same pool with other newer cryptocurrencies such as Solana (SOL) and Polkadot (DOT).
Cardano is in a much less comfortable position than its stepbrother Ethereum who has earned a stable spot on the stage. Solana has a bigger development team and seems to show even faster growth than Cardano, making many people reconsider their decision in investing in Cardano.
The steep competition brings another challenge: will Cardano continue to attract as many validators as it did before? Lower fees are a big plus for users, but it’s not the same view for the validators. More competition means more potential smart contacts. Smart contacts are generally preferred by the validators or miners because of their room for gains. Would the potential decrease in validators slow down Cardano’s operation?
New technology doesn’t mean perfect
Cardano was a big hit with PoS, but its “academic blockchain” isn’t perfect. A big risk with Cardano is that it’s a work in progress. Cardano isn’t entirely complete because it currently does not support smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
Not only is Ethereum equipped with these capabilities, but Binance Smart Chain (BSC) also brings it to the next level. Although Cardano has the promise to equip these functions, until then, Cardano faces one more big drawback.
How to Get Started
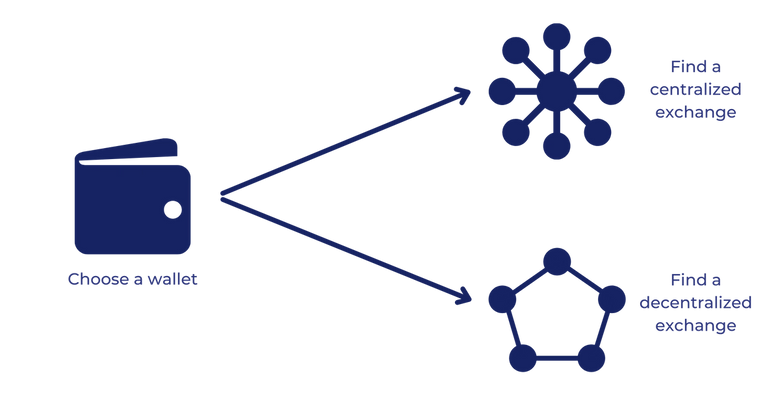
Choosing A Storage
Choosing a wallet is an important step to keep your assets safe. There are generally two types of wallets: hot wallets and cold wallets.
Hot wallets are any app on your phone, software on your computer, or any other web wallet that needs the internet to gain access. Hot wallets are digital and smarter than cold wallets, but the internet always brings a certain danger. If you access your hot wallet through an unsecured network, your information could be stolen. Unlike unauthorized bank transactions, you won’t be able to recover your coins.
Cold wallets are more old fashion, or perhaps a little incontinence to modern folks, but are definitely safer as long-term storage. Cold wallets can be hardware, USB drives, or just pens and papers with your access codes written down. The advantage with them is that they provide better security for your assets. The downside is they can be less accessible because you must physically have the paper or a computer/laptop with you. You won’t be able to access it easily on your phone at any time.
Choosing an Exchange
The next step is to find an exchange you prefer. You can choose from two types of exchanges: centralized exchanges and decentralized exchanges.
Considering whether the exchange offers Cardano can slip people’s minds. Not until the account is registered will they find out Cardano is not available at the platform they chose. For Bitcoin investors, this may be overlooked for a good reason: nearly every single cryptocurrency exchange offers Bitcoin. Cardano is not as widely acknowledged as Bitcoin, of course, making it a valid concern for investors.
Finding a centralized exchange
Centralized exchanges are relatively more popular because they're more familiar to the mass population. Some offer live monitors, arbitrage monitors, and often allow you to put out options. The fees for each exchange can vary widely based on the services offered.
To get started, you will need some of your personal information such as name and Social Security number. Based on your geographical location, the exchanges may ask you for your primary residence address.
Centralized exchanges accept debit cards, credit cards, and bank accounts as methods of payment. It's generally recommended to use a debit card or bank account with free cash flow if you can. It is typically best not to use a credit card to purchase investment products, especially products with high volatility such as cryptocurrencies. The return is not guaranteed, but the debts can grow exponentially.
Finding a decentralized exchange (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges may seem more fitting to trade decentralized products, but they are usually harder to navigate for beginners. These platforms are also more for trading than actual buy-ins.
The first generation of decentralized exchanges use order books to facilitate trade and determine the price. It’s more like centralized exchanges. They contain records of open buys and sell orders for each coin. Some examples of this older generation of DEX are Nash Exchange, dYdX, Binance DEX, and ViteX.
The newer generation of DEXs adjusts price with liquidity pools which are more efficient. They allow true instant peer-to-peer transactions to be executed. This instant transaction is referred to as a swap because the coins go from one trader’s wallets to another’s, like swapping. If that’s your preferred way of trading, examples of swap DEXs are Uniswap, SushiSwap, Gnosis, and DoDo.
Takeaways
Cardano is, by all means, a rising star to pay attention to. Its growing popularity and development in technology may eventually shorten its distance between the leaders. For beginners, Cardano may be a good cryptocurrency to start with.
There is always the risk Cardano may not outlive its competitors like Bitcoin did. Where Cardano will go in the long-term is not exactly clear. The disadvantages are also roadblocks it may or may not overcome in the long run. We can only wait and see how Cardano will perform in the near future. If you’re interested in investing in Cardano, carefully consider the risks and advantages it provides.
The information provided herein is for general informational purposes only and is not intended to provide tax, legal, or investment advice and should not be construed as an offer to sell, a solicitation of an offer to buy, or a recommendation of any security by Candor, its employees and affiliates, or any third-party. Any expressions of opinion or assumptions are for illustrative purposes only and are subject to change without notice. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results and the opinions presented herein should not be viewed as an indicator of future performance. Investing in securities involves risk. Loss of principal is possible.
Third-party data has been obtained from sources we believe to be reliable; however, its accuracy, completeness, or reliability cannot be guaranteed. Candor does not receive compensation to promote or discuss any particular Company; however, Candor, its employees and affiliates, and/or its clients may hold positions in securities of the Companies discussed.
